zkapps(零知识应用)是由零知识证明支持的 mina 协议智能合约,特别是 zk-snarks [零知识简洁非交互式知识论证]。zkapps 取代了 snapps [智能非交互式知识论证]应用]。 zkapp 智能合约是使用 o1js(typescript 库)编写的。 zkapps 在用户的 web 浏览器中运行客户端,并仅发布一个小的有效性证明,然后由 mina 节点进行验证。 zkapp 由智能合约和 ui 组成,我将在下一节中进一步描述。
应用
我创建了关于年龄验证的 zkapp,其中用户年龄在不干预个人数据的情况下得到验证。
我继续安装 zkapp-cli npm 包,它实际上创建了用于继续使用证明器函数和验证器函数的模板,作为 zk 证明构建过程的一部分
执行
下面是添加验证自定义逻辑的实现。它定义了 zk-snark 的电路逻辑,在证明生成过程中使用。实际的证明者函数由 o1js 库管理,并在使用私有输入在链外执行 zkapp 方法时调用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
import { field, smartcontract, state, state, method } from o1js;
/**
* private age verification contract
* the contract will verify if the users age is greater than or equal to the threshold age.
* the contract uses zero-knowledge proofs to keep the users age private.
*/
export class ageverification extends smartcontract {
// state variable to store the verification result (valid or invalid)
@state(field) valid = state<field>();
// method to initialize the state
init() {
super.init();
this.valid.set(field(0)); // default is invalid
}
// method to verify the age
@method async verifyage(age: field, threshold: field) {
// compute age - threshold
const difference = age.sub(threshold);
// use circuit-compatible logic to check if the difference is non-negative
const isvalid = difference.equals(field(0)).or(difference.greaterthanorequal(field(0)))
? field(1)
: field(0);
// set the validity of the verification result
this.valid.set(isvalid);
}
}
下面的脚本是一个与 ageverification zkapp 交互的测试套件。它在 txn.prove() 期间调用证明者逻辑,并通过检查其更新状态来验证 zkapp 的行为。
实际的证明者功能位于底层的 zkapp 方法(verifyage)中,txn.prove() 是在测试过程中生成证明的机制。
为了测试输入,我编辑了测试脚本,如下所示。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
import { accountupdate, field, mina, privatekey, publickey } from o1js;
import { ageverification } from ./ageverification; // import the correct contract
let proofsenabled = false;
describe(ageverification, () => {
let deployeraccount: mina.testpublickey,
deployerkey: privatekey,
senderaccount: mina.testpublickey,
senderkey: privatekey,
zkappaddress: publickey,
zkappprivatekey: privatekey,
zkapp: ageverification; // update to use ageverification instead of add
beforeall(async () => {
if (proofsenabled) await ageverification.compile(); // update compile for ageverification
});
beforeeach(async () => {
const local = await mina.localblockchain({ proofsenabled });
mina.setactiveinstance(local);
[deployeraccount, senderaccount] = local.testaccounts;
let feepayer = local.testaccounts[0].key;
deployerkey = deployeraccount.key;
senderkey = senderaccount.key;
zkappprivatekey = privatekey.random();
zkappaddress = zkappprivatekey.topublickey();
zkapp = new ageverification(zkappaddress); // instantiate ageverification contract
});
async function localdeploy() {
const txn = await mina.transaction(deployeraccount, async () => {
accountupdate.fundnewaccount(deployeraccount);
await zkapp.deploy();
});
await txn.prove();
// this tx needs .sign(), because `deploy()` adds an account update that requires signature authorization
await txn.sign([deployerkey, zkappprivatekey]).send();
}
it(generates and deploys the `ageverification` smart contract, async () => {
await localdeploy();
const valid = zkapp.valid.get(); // access the valid state variable
expect(valid).toequal(field(0)); // initially, the contract should set valid to field(0)
});
it(correctly verifies the age in the `ageverification` smart contract, async () => {
await localdeploy();
const age = field(25); // example age value
const threshold = field(18); // example threshold value
// call the verifyage method
const txn = await mina.transaction(senderaccount, async () => {
await zkapp.verifyage(age, threshold); // use the verifyage method
});
await txn.prove();
await txn.sign([senderkey]).send();
const valid = zkapp.valid.get(); // check the validity state after verification
expect(valid).toequal(field(1)); // expected to be valid if age >= threshold
});
});
以下是测试结果
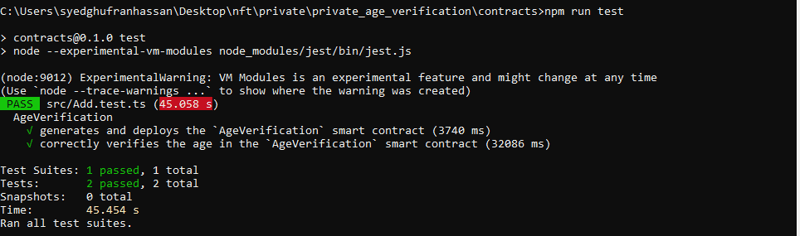
我在interact.ts文件中添加了证明者机制,它基本上生成一个zk-snark证明,并在mina区块链
中进行交易时提交证明。当 interact.ts 脚本生成证明时,验证是在处理交易时由 mina 区块链执行的。这是 zk-snark 系统的一个关键方面,证明者生成验证者(mina 网络)检查的证明。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
import fs from fs/promises;
import { Mina, NetworkId, PrivateKey, Field } from o1js;
import { AgeVerification } from ./AgeVerification;
// check command line arg
let deployAlias = process.argv[2];
if (!deployAlias)
throw Error(`Missing <deployAlias> argument.
Usage:
node build/src/interact.js <deployAlias>
`);
Error.stackTraceLimit = 1000;
const DEFAULT_NETWORK_ID = testnet;
// parse config and private key from file
type Config = {
deployAliases: Record<
string,
{
networkId?: string;
url: string;
keyPath: string;
fee: string;
feepayerKeyPath: string;
feepayerAlias: string;
}
>;
};
let configJson: Config = JSON.parse(await fs.readFile(config.json, utf8));
let config = configJson.deployAliases[deployAlias];
let feepayerKeysBase58: { privateKey: string; publicKey: string } = JSON.parse(
await fs.readFile(config.feepayerKeyPath, utf8)
);
let zkAppKeysBase58: { privateKey: string; publicKey: string } = JSON.parse(
await fs.readFile(config.keyPath, utf8)
);
let feepayerKey = PrivateKey.fromBase58(feepayerKeysBase58.privateKey);
let zkAppKey = PrivateKey.fromBase58(zkAppKeysBase58.privateKey);
// set up Mina instance and contract we interact with
const Network = Mina.Network({
// We need to default to the testnet networkId if none is specified for this deploy alias in config.json
// This is to ensure the backward compatibility.
networkId: (config.networkId ?? DEFAULT_NETWORK_ID) as NetworkId,
mina: config.url,
});
const fee = Number(config.fee) * 1e9; // in nanomina (1 billion = 1.0 mina)
Mina.setActiveInstance(Network);
let feepayerAddress = feepayerKey.toPublicKey();
let zkAppAddress = zkAppKey.toPublicKey();
let zkApp = new AgeVerification(zkAppAddress);
let age = Field(25); // Example age
let threshold = Field(18); // Example threshold age
// compile the contract to create prover keys
console.log(compile the contract...);
await AgeVerification.compile();
try {
// call verifyAge() and send transaction
console.log(build transaction and create proof...);
let tx = await Mina.transaction(
{ sender: feepayerAddress, fee },
async () => {
await zkApp.verifyAge(age, threshold); // Replacing update() with verifyAge
}
);
await tx.prove();
console.log(send transaction...);
const sentTx = await tx.sign([feepayerKey]).send();
if (sentTx.status === pending) {
console.log(
Success! Age verification transaction sent.
+
Your smart contract state will be updated +
`
as soon as the transaction is included in a block:` +
`
${getTxnUrl(config.url, sentTx.hash)}`
);
}
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
}
function getTxnUrl(graphQlUrl: string, txnHash: string | undefined) {
const hostName = new URL(graphQlUrl).hostname;
const txnBroadcastServiceName = hostName
.split(.)
.filter((item) => item === minascan)?.[0];
const networkName = graphQlUrl
.split(/)
.filter((item) => item === mainnet || item === devnet)?.[0];
if (txnBroadcastServiceName && networkName) {
return `https://minascan.io/${networkName}/tx/${txnHash}?type=zk-tx`;
}
return `Transaction hash: ${txnHash}`;
}
我使用的年龄和阈值输入为 25 和 18。
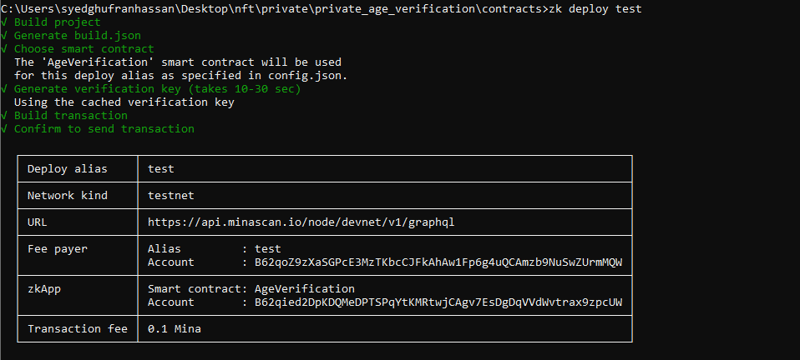
由于测试已通过运行 npm run test 成功完成。我继续使用 zk config 在 devnet 上进行部署
部署别名:test
网络类型:测试网
网址:https://api.minascan.io/node/devnet/v1/graphql
付费者:新的付费者密钥
交易:0.1可以从这里检索 url:
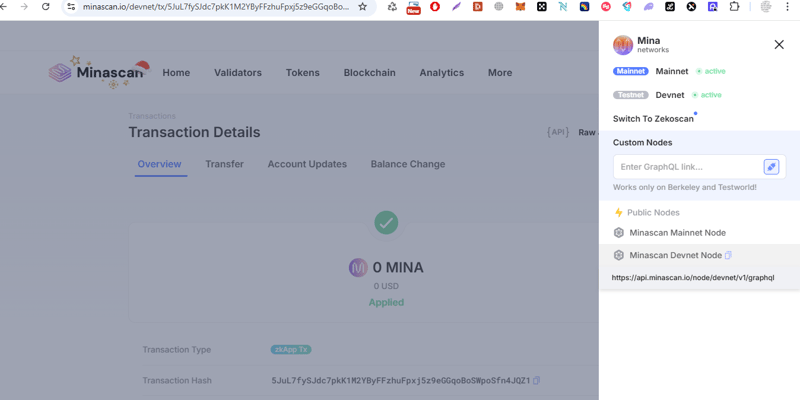
然后在部署后我得到了以下响应。
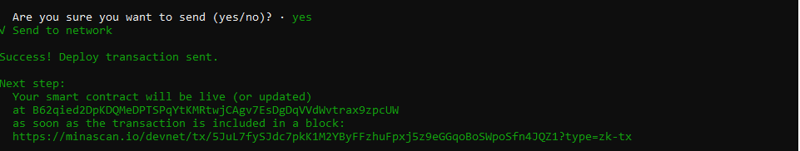
合约部署在以下devnet
部署后,我继续使用 ui,通过提供 rpc url 和部署的合约地址,选择简单的 html、css 和 js,这是最终的 ui。
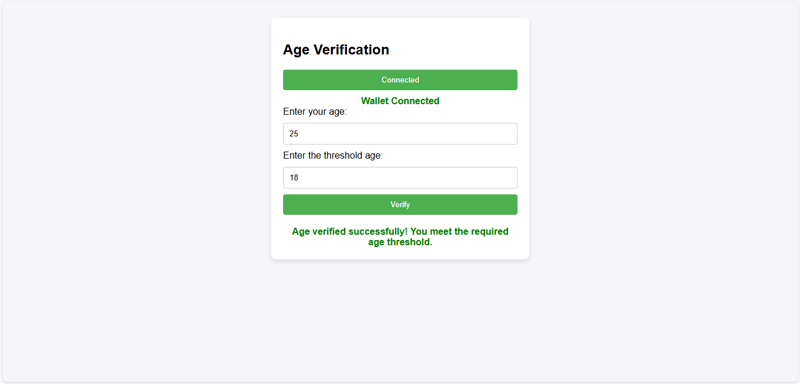
将智能合约与ui集成后zkapp的创建就完成了。在为 ageverification zkapp 构建用户界面 (ui) 后,前端与智能合约的集成允许用户与零知识证明系统无缝交互。 ui 有助于向合约提交用户年龄和阈值数据,同时通过 zk-snark 维护隐私。这使得用户能够在不透露实际值的情况下验证自己的年龄,从而保持机密性。后端利用证明者功能生成证明,mina 区块链对其进行有效验证。这种端到端解决方案可确保安全、用户友好的体验,同时充分利用 mina 基于 zk-snark 的架构提供的隐私和可扩展性功能。
以上就是探索 Mina 协议:zk 应用程序的实际用例的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

